What Are the Benefits of Busbar Power Distribution?

October 21, 2024
The adoption of busbar power distribution systems on a global scale has accelerated in the last few years. In fact, research estimates that the market for copper busbar power panels in North America alone will grow by nearly 7.5% annually through 2032.
There are several factors that account for this growth and why manufacturers are moving fast to harness the benefits of busbar power, but safety and efficiency are two of the biggest drivers.
Busbar helps reduce arc flash
There are roughly 30,000 arc flash incidents in the United States each year, many of which are powerful enough to cause significant injury to workers and costly damage to equipment.
This is pushing regulatory agencies to revise compliance guidelines. The short-circuit current ratings (SCCR) index outlines the appropriate level of short-circuit current electrical equipment can carry to help avoid electrical fault or arc flash, and recent changes to the SCCR have made it challenging for manufacturers to safely install and operate traditional block-and-cable power distribution.
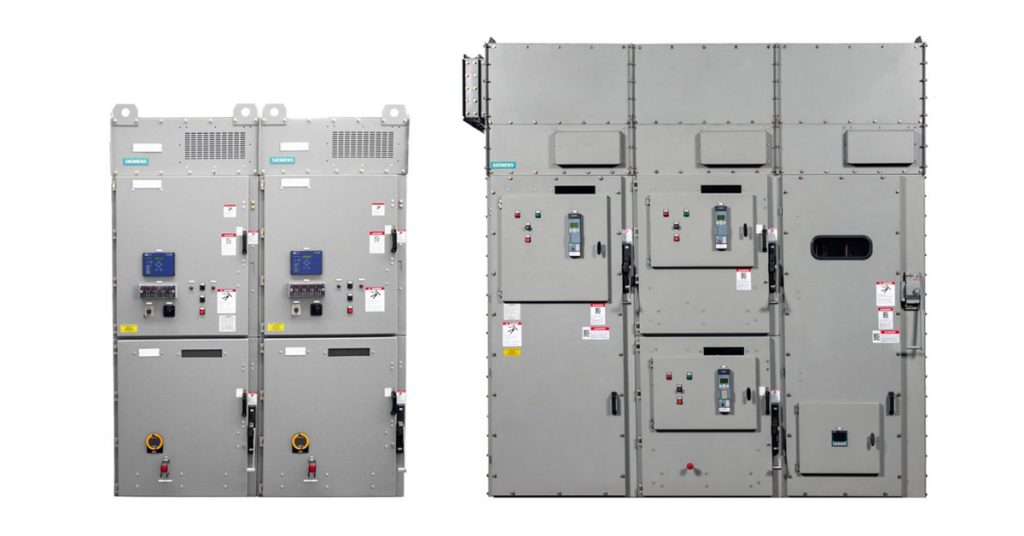
Whereas the cumbersome nature of traditional power distribution is more likely to produce electrical fault, the simplified design of busbar power panels offers touch-safe operation. This drastically reduces the risk of electrical fault to help protect workers and automation equipment.
Busbar is more efficient than traditional power distribution
While compliance and safety are major players in the move to busbar power, the need to optimize the use of space inside an industrial enclosure and the demand for faster, more efficient configuration and installation are also important factors in the transition to busbar power.
Traditional panel wiring systems — referred to as block-and-cable systems — are designed around large power distribution blocks (PDBs) that require large parallel cables. Each PDB feeds a specific part of the control panel, which, as enclosures continue to require more power in service of facilitating larger manufacturing programs, means more PDBs and less space and flexibility inside the enclosure.
Busbar power, on the other hand, utilizes a conductive copper or aluminum strip or bar that distributes electricity to multiple circuits in a parallel configuration. These pre-configured conductive strips or bars can be connected to create systems of varying length based on the amount of power the control panel requires.