How Manufacturers Can Go Unwired to Unleash Unlimited Possibilities

March 31, 2022
By Oliver Wang, Product Marketing Manager, Edge Connectivity and Computing, Moxa
Where it’s difficult to hardwire industrial operations to ensure time to market, industrial wireless LANs (WLANs) provide an ideal alternative to traditional wired Ethernet LANs. Indeed, recent advances in wireless technology have contributed to industrial WLANs becoming commonplace solutions in automotive plants, warehouses, and transportation systems, among others, where automated equipment is required that is constantly moving or difficult to wire. Industrial WLANs enable these types of systems to be connected for enhanced operational efficiency.
With so much potential waiting to be unlocked by cutting free from wires, it’s no wonder the popularity of industrial WLAN applications has grown so rapidly in recent years, and is now expected to reach nearly $40 billion (USD) by 2026. For instance, you can use WLAN technology to deploy automated forklifts in a smart warehouse or overhead transfer system to increase efficiency and productivity, making the best use of limited manpower.
As endless as the possibilities maybe, however, going wireless isn’t always a clear-cut choice. Even if you’ve decided on a wireless LAN, how do you choose the right solution for your industrial requirements? Consider the following criteria from Moxa.
Key Criteria for Choosing Industrial WLAN Devices
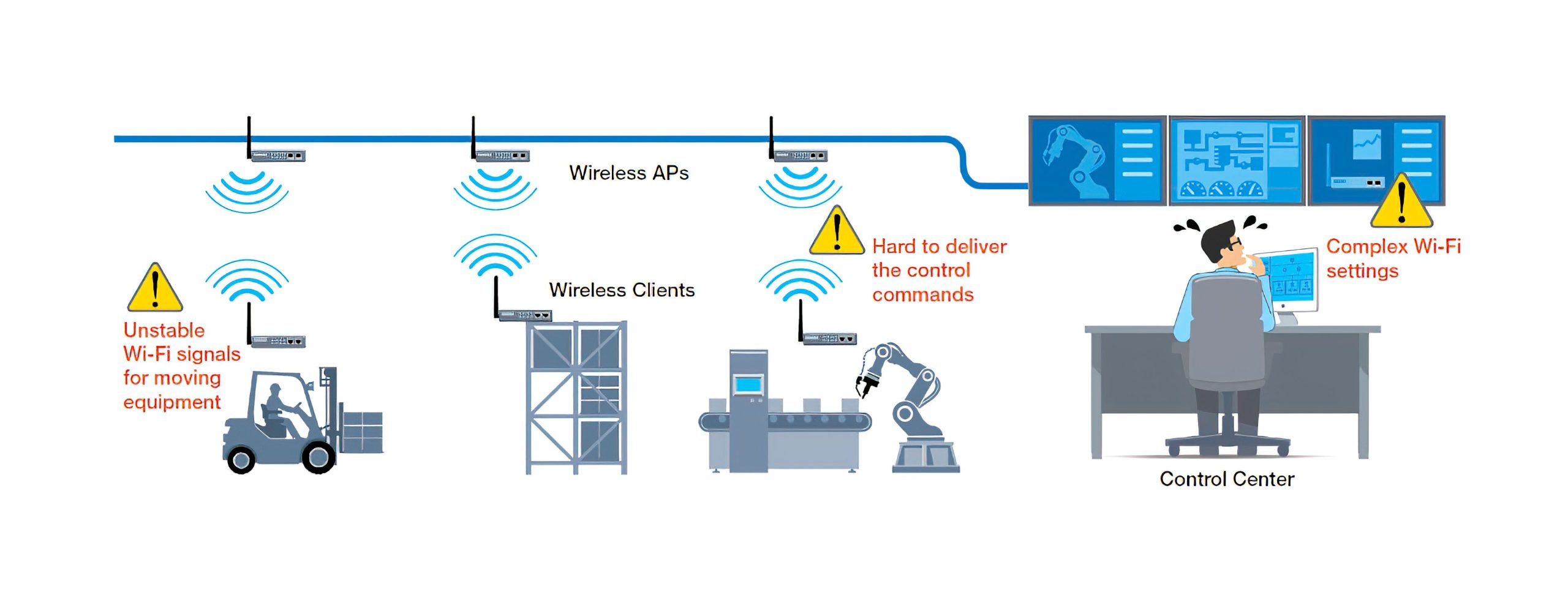
Without a doubt, industrial wireless LANs can extend connectivity beyond traditional physical limits and boundaries, unleashing new possibilities. However, industrial engineers may hesitate to embrace wireless applications due to a number of different hurdles. How do you confirm that the network is indeed connected when wireless connections are invisible? How do you troubleshoot when these invisible connections go down? Such concerns are relevant more than ever since IIoT applications require systems to be connected into one converged network. Any single point of failure can be fatal for the entire network. Besides thoroughly planning your wireless network design, here are some key criteria for choosing industrial WLAN devices and suggestions for how to address common concerns.
Wi-Fi Availability Is the First Priority
Industrial WLAN devices require specialized technology to establish and ensure reliable wireless networks. This is because wireless connection quality can be affected by many different issues, such as radio frequency (RF), interference in an industrial environment, incorrect antenna configuration, signal strength over long distances, and so on. Failing to properly design your system to avoid such issues can result in unstable communications, or even permanently damage your devices and cause a complete shutdown of your system.
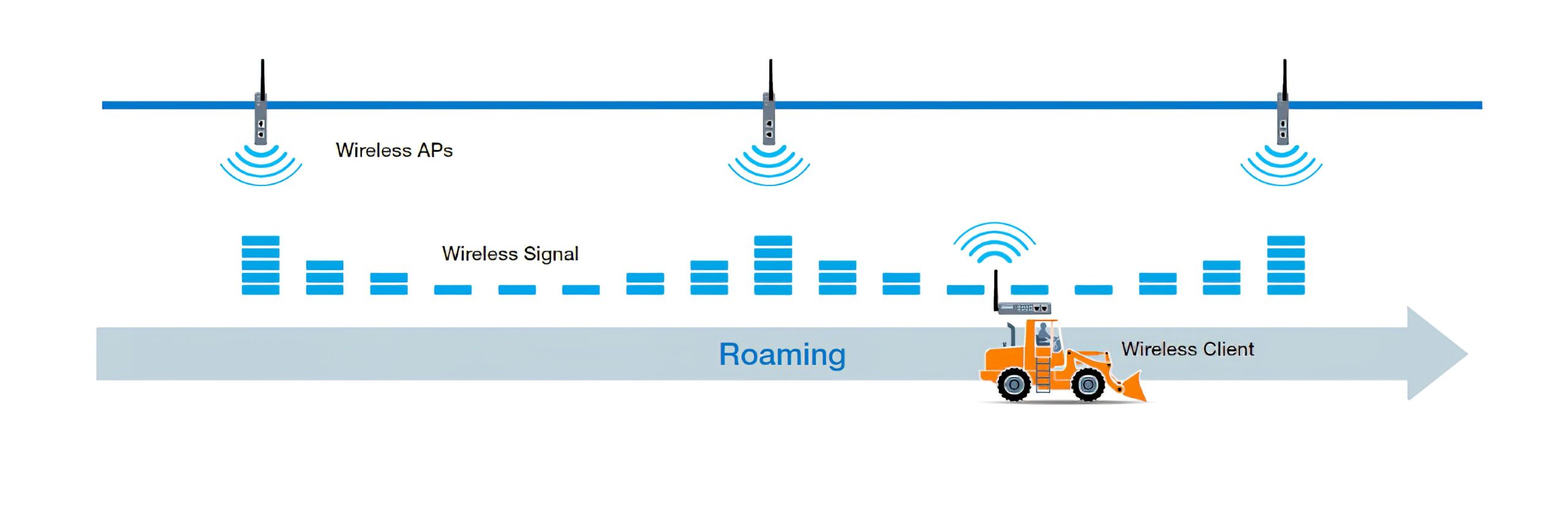
In addition, constantly moving equipment requires extra attention to roaming requirements. For example, even if you have a strong wireless signal on your AP, moving devices to a different location may require a greater transmission signal, resulting in slower Wi-Fi connections or even network failures. Since slow or failed connections are unacceptable in industrial environments, consider advanced wireless roaming technologies that can achieve millisecond-level roaming to ensure reliable wireless connections.
Minimal Effort on Wi-Fi Settings
Whether you are implementing a wireless network for the first time or have numerous WLAN deployments under your belt, you always want to choose easy-to-use solutions. Although wireless connections make constructing network infrastructure more convenient, network setup and long-term maintenance can also have a big impact on user experience. When it comes to basic device configuration during the initial setup stage for deploying or maintaining a network, a powerful software tool can save you significant time and effort. Once the networks are up and running, a software tool that can configure all your devices easily and find the best Wi-Fi channels to use in your environment with a click of a mouse can help keep your wireless connections stable and take the headache out of network administration.
Don’t Let Protocol Compatibility Issues Hold You Back
Many WLAN devices are deployed in various industrial applications, including automatic guided vehicles (AGVs) and forklifts in logistics systems. These systems require sophisticated devices such as sensors and PLCs to determine the location of moving vehicles. It is essential to ensure seamless communications between PLCs and control centers for safety reasons. When industrial equipment such as PLCs connect to a wireless client, a common issue is whether the wireless client device can support certain industrial protocols, such as PROFINET. To ensure seamless industrial protocol communications, consider the following requirements:
- 1. Layer 2 transparency over WLAN
- 2. Communication latency that meets your application requirements
These three key criteria have been distilled from many years of experience in enabling industrial connectivity for customers around the world.
![]()
To learn more about industrial IEEE 802.11n wireless AP/bridge/clients specifically designed to overcome the challenges of industrial applications, visit the literature section of the Moxa website.